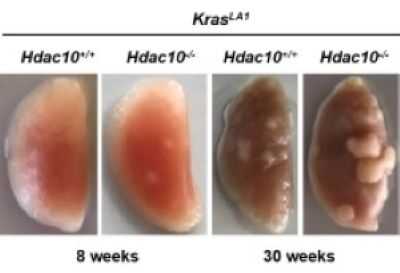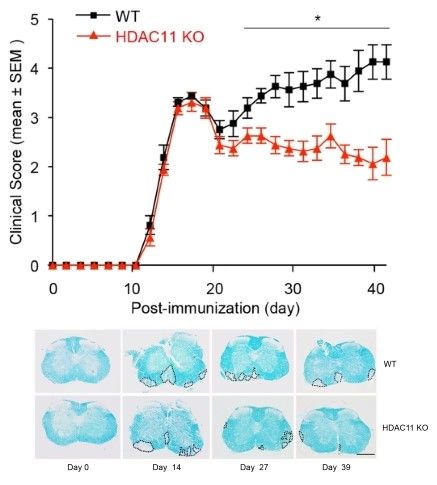
The Seto Lab has a long-standing interest in gene regulation and histone deacetylases (HDACs). Early on, we discovered and cloned HDAC2 and HDAC3 enzymes and performed detailed analyses of these proteins. Over the last 25 years, we have been actively studying many different aspects of histone deacetylation, including the dissection of all 18 human HDACs. Our work has led to seminal discoveries regarding regulation of histone deacetylation and identification of key non-histone targets of the HDAC enzymes. More recently, our work has extended to the analysis of how the activities/functions of histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and HDACs are interrelated, elucidating the role of HDACs in anti-tumor immunity, and identifying HDAC-specific inhibitors for disease treatments.